What is a SWOT Analysis?
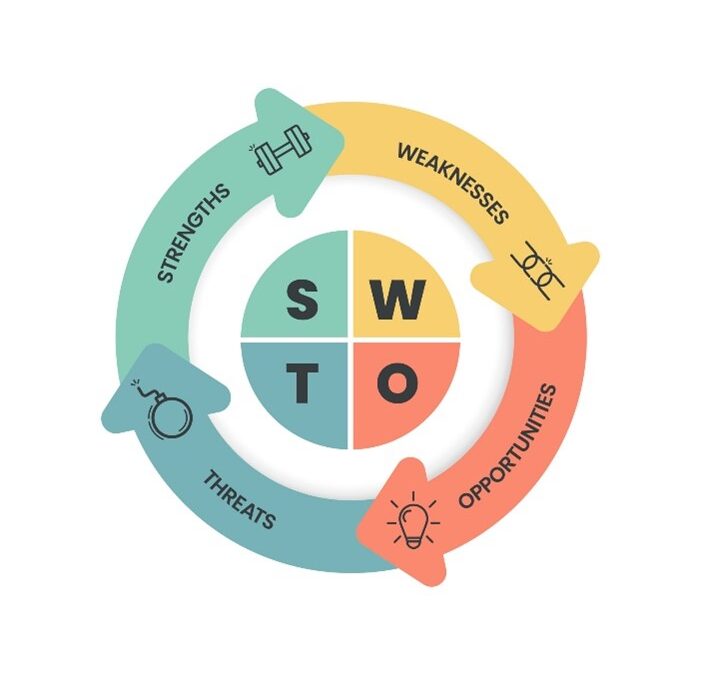
A SWOT analysis is a planning tool to evaluate your business. It is usually portraited into 4 quadrants as per below:

The top two quadrants are the internal factors of the business while the bottom two quadrants are the external factors.
- The internal factors: These are the Strengths (S) and Weaknesses (W) of the company.
It is the STRENGTHS which will provide you with the competitive advantage over your competitors. These are the positive factors that you do well which are in your control. Strength could be that you have a loyal customer base or the strong brand that you have created for the business.
WEAKNESSES on the other hand are the negative factors which are in your control It is the things that you not doing well. Example of weaknesses is that the business has high level of debts or have a tarnished brand.
- The external factors: These are the Opportunities (O) and Threats (T) of the company
OPPORTUNITES are the positive factors that are outside of your control such as reduction in tariffs, use of new technologies bringing efficiencies, expand current operations. It is the ‘Opportunities’ that provide the large possibilities into the company
THREATS are the negative factors which are outside you control. These are the things that can hurt you such as a new competitor into the market or new government regulation…just to name a couple.
Preparing a SWOT Analysis
Through a SWOT analysis, you will be able to determine what you do well, and which areas require greater attention. With the internal factors, you want to build on your strengths while eliminating or at least reducing your weaknesses. A well thought-out and executed SWOT analysis will be able to turn your weakness into a potential strength. Regarding the external factors, you need to take action on opportunities and counter-act any threats.
When preparing a SWOT analysis ask yourself the following questions:
- What is my business’ competitive advantage?
- What does the business do well?
- What skills and knowledge do you and your staff have? Do they need to be upskilled?
- What are the systems and processes that you are utilising. Are they a strength or are they a weakness which need to be improved?
- How are the staff performing? Do you have a high turnover rate or high absentee rate?
- Are there any new market opportunities or greater innovation opportunities?
- Are there new competitors in the market? What are they doing differently?
- Are there any other external factors which can affect the business. Consider political, environmental, and legislative requirements.
SWOT Examples
(S) Strengths
|
(W) Weaknesses
Low profitability |
(O) Opportunities
|
(T) Threats
Economic downturn |
When should a SWOT Analysis be introduced?
A well-executed SWOT analyses requires resources and time to ensure effectiveness, therefore it should only be created for specific purposes

SWOT can add great value:
- When you launch something new (e.g. a new product / service offering)
- If you want to determine areas in which the business can grow or improve
- Whenever you want to review the overall business performance
A SWOT should always be carried out before any major change!
How to write an effective SWOT Analysis?
You want to ensure that you have a thorough SWOT. Here are a few ideas which will help create an effective SWOT:

1. Internal Factor Assessment
The internal factors (that is the strengths and weaknesses) tend to be easier to identify, solve as you have much more control over them. So, focus on your internal strengths and weaknesses. Once you know what they are, you can determine ways building on the strengths and reducing the weaknesses.
2. Review the External Factors
These are your opportunities and threats which start from processes outside your control. Typical elements include competitors, market trends, regulatory framework, environmental factors and anything else affecting the business from the outside.
3. Brainstorm and be Creative.
One great way to become innovative is to have brainstorming sessions. These generally inspires creativity. Invite staff from different areas to share their ideas and throughts.
4. Prioritise
Once all these great ideas which create opportunities have been brought to the table, they need to be ranked in order. Talk and work through each respective idea. You can then assess which are the best ideas to work on. You need to consider the competency of the staff to execute the idea, the capabilities of the business and the overall performance it will have.
5. Implement
You may think that the hard work has been completed but you are just at the beginning. Ideas are great but nothing will change unless action is taken. Now is the time that you develop a structure to execute the ideas.
SWOT Analysis – The 4 step process

STEP 1: CONDUCT A DOCUMENT REVIEW
This will allow the business owner, manager of external consultant to understand the business’ mission and the area chosen to prepare the SWOT analysis meeting.
STEP 2: DEFINE THE FRAMEWORK
This will focus on a specific area that will be analysed and reviewed. That is, you may not concentrate on the business as a whole but focus on a specific department, location, area etc.
STEP 3: IDENTITY THE SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats).
The S,W,O,T are the components and under each component define a minimum of 3 elements. Each element should be based on facts.
STEP 4: PRIORITISE
Once you have identified the elements within the components, you need to prioritise these elements and provide solutions. What will be selected first is generally based on three factors:
- How closely does it correlate to the business’ mission?
- What is the expected performance?
- How easy is it to implement?
HOW CAN WE HELP?
If you require any assistance with developing a SWOT analysis or any other finance related matters, feel free to contact our team of experts or submit and online enquiry form to ‘Growth Pathways’